
Navigating the AI Transformation Landscape
Artificial intelligence has moved from buzzword to business imperative in boardrooms across industries. The potential for AI to transform enterprise operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation is undeniable—but behind the excitement lies a sobering reality: despite significant investments, many organizations struggle to realize tangible value from their AI initiatives.
A recent study shows that 74% of companies struggle to achieve value from their AI initiatives. This isn’t because the technology doesn’t work – it’s because implementation strategies often fall short. The disconnect between AI’s promise and practical results often stems not from the technology itself, but from inadequate implementation strategies, misaligned priorities, and a lack of organizational readiness.
This blog aims to offer a practical roadmap for AI implementation in enterprise IT and cut through the hype and providing business leaders with a practical roadmap for AI implementation—one built on strategic focus, measurable outcomes, and sustainable practices.
The Current State of Enterprise AI: Beyond the Buzz
The AI landscape has evolved dramatically in recent years, particularly with the emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) and generative AI capabilities that have captured both public attention and corporate investment.
The Acceleration of AI Adoption
The past year has witnessed unprecedented acceleration in AI adoption across enterprises. AI adoption is accelerating across industries. Generative AI use alone jumped from 33% in 2023 to 71% in 2024, signaling a seismic shift in how organizations approach emerging technologies.
Yet adoption rates tell only part of the story. What matters more is the quality of implementation and the tangible impact on business outcomes. Every company has an AI project; far fewer have an AI strategy.
The Value Gap: Why Most AI Initiatives Fall Short
The primary reason AI projects fail to deliver expected returns isn’t technological limitations—it’s strategic and operational shortcomings.
Research shows that implementation challenges break down as follows:
- 70% stem from people and process issues
- 20% come from technology problems
- Only 10% relate to the AI algorithms themselves
Common pitfalls include:
- Fragmented approaches: Pursuing isolated use cases without an integrated strategy
- Technology-first thinking: Overemphasizing algorithm performance while neglecting people and processes
- Inadequate infrastructure: Building on shaky foundations of poor data quality and integration
- Talent constraints: Struggling to acquire and retain AI expertise in a competitive market
- Governance gaps: Lacking frameworks for responsible development and deployment
As we’ll explore, addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach that balances technical excellence with organizational readiness.
The Cornerstones of an Effective AI Roadmap
A successful AI implementation begins with establishing clear foundations. Based on our analysis of high-performing AI initiatives across industries, we’ve identified five cornerstones that form the basis of an effective enterprise AI roadmap.
1. Strategic Alignment: Connecting AI to Business Objectives
Unlike general-purpose technologies of the past, AI applications must be tightly aligned with specific business objectives to deliver measurable value. This requires cross-functional collaboration between technology teams and business stakeholders from the outset.
Organizations that do this see an average return of $3.70 for every $1 invested.
Begin with a workshop that brings together executives, business unit leaders, and technical teams to identify high-value opportunities where AI can address existing pain points or create new capabilities.
2. Foundation Building: Data Infrastructure and Governance
AI systems are only as good as the data that powers them. Before implementing sophisticated models, organizations must ensure they have the necessary data infrastructure, quality controls, and governance frameworks in place.
The four foundational components required for enterprise AI implementation are:
- High-quality data (structured or unstructured)
- Machine learning systems (typically running on cloud platforms)
- Sufficient compute power (especially GPUs)
- Security and governance frameworks
Conduct a comprehensive data readiness assessment to identify gaps in data quality, integration capabilities, and governance processes before committing to specific AI implementations.
3. Capability Development: Building for the Long Term
Sustainable AI value creation requires developing internal capabilities rather than merely outsourcing implementation. This includes not just technical expertise, but also business domain knowledge, change management skills, and a culture of experimentation.
Develop internal capabilities instead of just outsourcing. Follow these steps:
- Analyze your business to find AI opportunities
- Define clear use cases with specific value metrics
- Qualify use cases based on business value and feasibility
- Build a prioritized implementation roadmap
Invest in a combination of hiring, training, and strategic partnerships to build a balanced team with both technical AI expertise and domain-specific business knowledge.
4. Implementation Strategy: From Pilots to Production
Moving AI from concept to production requires a carefully structured approach that balances innovation with pragmatism. The most successful implementations typically follow a staged progression:
- Pilot phase: Testing hypotheses in controlled environments
- Proof of value: Demonstrating measurable business impact
- Scale phase: Expanding successful implementations across the organization
- Integration: Embedding AI capabilities into core business processes
Begin with 2-3 high-potential use cases that can demonstrate value within 3-6 months, establishing quick wins that build momentum for broader adoption.
5. Responsible AI: Ethics and Governance by Design
As AI becomes more deeply embedded in business operations, ensuring ethical implementation becomes not just a moral imperative but a business necessity. Organizations must establish clear governance frameworks that address issues such as bias, transparency, accountability, and privacy.
Establish clear ethical guidelines and governance processes.
Address these key areas:
- Digital amplification (how AI extends reach and influence)
- Algorithmic bias (preventing discrimination)
- Cybersecurity (protecting against vulnerabilities)
- Privacy (safeguarding sensitive data)
- Inclusiveness (ensuring equitable access)
Establish an AI ethics committee with diverse representation from technical, business, legal, and compliance teams to review all significant AI implementations before deployment.
Practical Implementation: A Phased Approach
With the foundational cornerstones in place, organizations can move toward implementation. The following phased approach balances quick wins with long-term capability building.
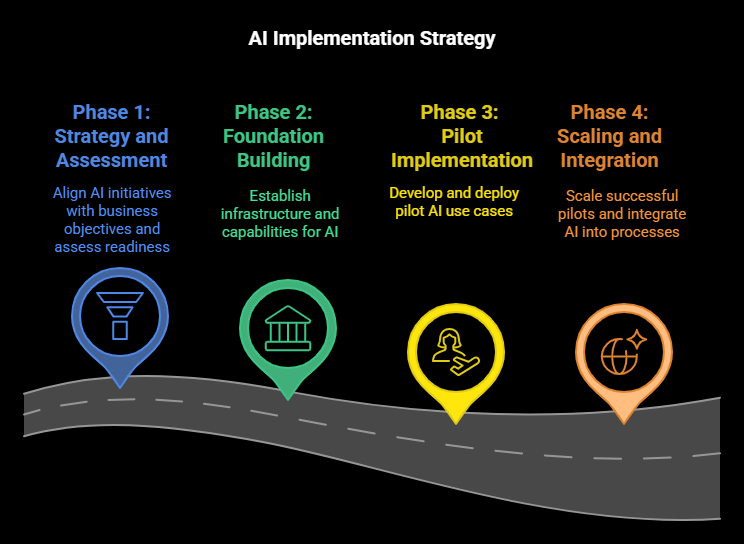
Phase 1: Strategy and Assessment (1-2 Months)
The first phase focuses on aligning AI initiatives with business objectives and establishing a baseline understanding of organizational readiness.
Key Activities:
- Conduct an AI readiness assessment (data, technology, talent, processes)
- Identify and prioritize potential use cases based on business impact and feasibility
- Define clear success metrics for each prioritized use case
- Establish a governance framework for AI development and deployment
Phase 2: Foundation Building (2-3 Months)
The second phase involves establishing the necessary infrastructure, data resources, and organizational capabilities to support successful AI implementation.
Key Activities:
- Enhance data quality, accessibility, and integration capabilities
- Build or upgrade cloud infrastructure for AI workloads
- Develop internal AI literacy through training and awareness programs
- Create cross-functional teams combining technical expertise with domain knowledge
Phase 3: Pilot Implementation (3-4 Months)
The third phase focuses on developing and deploying pilot implementations for the highest-priority use cases, with an emphasis on learning and iteration.
Key Activities:
- Develop proofs of concept for 2-3 high-priority use cases
- Implement in controlled environments with clear success metrics
- Gather user feedback and performance data
- Iterate based on learnings and refine the implementation approach
Phase 4: Scaling and Integration (4-6 Months)
The final phase involves scaling successful pilots across the organization and integrating AI capabilities into core business processes.
Key Activities:
- Scale successful pilots to full production environments
- Integrate AI capabilities with existing business systems and workflows
- Establish monitoring and maintenance processes
- Develop a center of excellence to support ongoing AI initiatives
Implementation Challenges and How to Address Them
Even with a well-structured roadmap, enterprises will inevitably face challenges in their AI implementation journey. Understanding and proactively addressing these challenges is essential for long-term success.
Data Quality and Integration Issues
Challenge: Poor data quality, siloed information systems, and integration difficulties remain the most common technical barriers to successful AI implementation.
Solution Approach:
- Conduct a comprehensive data audit to identify quality issues and gaps
- Implement master data management practices to ensure consistency
- Invest in data integration platforms that can connect disparate sources
- Consider a federated data approach that balances centralization with flexibility
Talent and Capability Gaps
Challenge: The scarcity of AI expertise—from data scientists to ML engineers—continues to constrain implementation efforts, with 78% of organizations citing talent shortages as a significant barrier.
Solution Approach:
- Develop a balanced talent strategy combining hiring, upskilling, and partnerships
- Create cross-functional teams that pair technical experts with domain specialists
- Implement a “hub and spoke” model with a central AI team supporting business units
- Invest in no-code/low-code AI platforms to democratize development capabilities
Change Management and Adoption
Challenge: Resistance to new AI-powered tools and processes often stems from fear, unfamiliarity, or concerns about job displacement, significantly hampering implementation timelines.
Solution Approach:
- Involve end users early in the design and testing process
- Communicate a clear vision that emphasizes augmentation rather than replacement
- Provide comprehensive training and support during the transition
- Recognize and celebrate early adopters and success stories
Ethical and Governance Concerns
Challenge: As AI becomes more prevalent, organizations face increasing scrutiny regarding bias, transparency, privacy, and compliance with emerging regulations.
Solution Approach:
- Establish a cross-functional AI ethics committee with diverse representation
- Implement rigorous testing protocols for bias detection and mitigation
- Develop clear documentation standards for model development and deployment
- Create transparency mechanisms that explain AI decisions to stakeholders
Looking Ahead: Emerging Trends in Enterprise AI
As we navigate the current landscape of enterprise AI implementation, it’s valuable to consider emerging trends that will shape the future. These developments will influence how organizations approach AI strategy and implementation in the coming years.
The Rise of AI Agents and Automation
AI is evolving from isolated point solutions to integrated agents capable of executing complex workflows across multiple systems. These agents can handle everything from customer service inquiries to internal process automation with minimal human intervention.
Organizations should begin exploring agent-based architectures that can orchestrate multiple AI capabilities to solve end-to-end business processes rather than isolated tasks.
AI-Human Collaboration Models
Rather than replacing human workers, the most successful AI implementations will focus on augmenting human capabilities through effective collaboration models. This approach maximizes both AI’s computational power and human judgment.
Focus on designing AI systems that enhance human capabilities rather than simply automating existing roles, with clear mechanisms for human oversight and intervention.
Multimodal AI Integration
The future of enterprise AI involves seamless integration of multiple modalities—text, images, audio, video, and sensor data—to provide more comprehensive and context-aware capabilities.
Begin exploring multimodal AI applications in areas like customer service, product development, and operations, where combining different data types can provide richer insights.
Democratization of AI Development
Low-code and no-code AI platforms are making sophisticated capabilities accessible to business users without deep technical expertise, accelerating adoption and innovation.
This trend is evidenced by the proliferation of tools like Microsoft’s Copilot, which reduced report creation time by 82% by enabling non-technical users to leverage AI capabilities.
Implement platforms that enable business users to create AI-powered solutions while maintaining appropriate governance guardrails.
Enhanced Focus on Responsible AI
As AI becomes more pervasive, the importance of ethical, transparent, and accountable implementation will only increase, driven by both regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
Establish robust, responsible AI frameworks early, treating ethical considerations as fundamental design requirements rather than afterthoughts.
From Vision to Value
The journey toward effective enterprise AI implementation is neither simple nor quick, but the potential rewards are substantial. Organizations that develop a strategic, disciplined approach—focusing on business value, building strong foundations, and addressing people and process challenges—consistently outperform their peers in realizing tangible benefits from AI investments.
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, successful implementation requires more than technical expertise. It demands strategic alignment, organizational readiness, careful change management, and ethical governance. By following the practical roadmap outlined here and learning from real-world examples, business leaders can navigate the complexity of AI transformation and unlock its true potential.
The most important insight may be this: AI implementation is not a one-time project but an ongoing capability-building journey. The organizations that will thrive in the AI-enabled future are those that develop the ability to continuously experiment, learn, adapt, and scale—embedding artificial intelligence not just in their technology stack but in their fundamental approach to creating value.
As your organization embarks on or continues its AI implementation journey, remember that the goal is not simply to deploy the latest technology but to create sustainable business value through the thoughtful application of AI capabilities to your most important challenges and opportunities.
This blog is part of our ongoing series on enterprise technology transformation. For more insights on building effective digital capabilities, visit our insights page or contact our advisory team.



